7 Things You Should Never Leave in Your Car During Winter

Winter brings a whole new set of challenges for car owners, and it’s not just about keeping your engine running smoothly. When the temperatures drop, leaving certain items in your car can lead to damage, safety risks, and unnecessary expenses. Whether you’re running errands or just parked for a while, some belongings should never be left inside your car during the winter months. From electronics to medications, the cold can affect more than just your car. Here are seven things you should always take with you instead of leaving in your vehicle during the winter.
1. Electronics and Gadgets

You might think your smartphone or tablet can handle the cold, but extreme temperatures can do serious damage to your electronics. The batteries in devices like smartphones, cameras, and laptops can freeze and lose their charge more quickly when exposed to frigid temperatures. In some cases, condensation inside your device when you move it from the cold car to a warm place can short-circuit internal components, making it unusable. Not to mention, leaving electronics in your car can make them easy targets for thieves. The best way to protect your gadgets is to keep them inside where it’s warm and safe.
2. Bottled Water and Beverages

It might seem harmless to leave a bottle of water or a beverage in your car, but the cold can cause big problems. When liquids freeze, they expand, which can cause plastic bottles to crack or burst. Glass bottles are even more vulnerable, as the liquid inside them can freeze and shatter the container. Besides creating a mess, frozen beverages lose their taste and can be unsafe to consume after they’ve been thawed and refrozen. To prevent this from happening, always bring your drinks indoors when you leave your car.
3. Medications

Your health should always come first, and that means taking extra care with your medications during the winter. Many medications, especially liquids like insulin, are temperature-sensitive and can lose their effectiveness or even become dangerous if exposed to extreme cold. The cold can cause condensation to form in medication containers, potentially leading to mold or degradation of the product. Keep your medications in a temperature-controlled environment to ensure they remain safe and effective. If you’re traveling with them, make sure they stay with you in a warm bag or pocket.
4. Canned Foods

While canned foods are great for stockpiling emergency supplies, they don’t fare well in freezing temperatures. The liquid inside the can can expand as it freezes, causing the can to bulge or even burst open. Even if the can doesn’t break, freezing can alter the texture and taste of the food inside. This can lead to an unpleasant eating experience or, worse, food that’s no longer safe to consume. To avoid dealing with these problems, keep canned goods inside your home or in a temperature-stable location, especially during the colder months.
5. Aerosol Cans

Aerosol cans, like deodorants, air fresheners, or spray paints, should never be left in your car when the weather turns cold. The pressurized contents inside the cans are vulnerable to temperature extremes. When exposed to freezing temperatures, the internal pressure can decrease, and if the can warms up or is shaken, it could cause an explosion. Not only could this create a mess, but it could also be hazardous. For your safety and to protect your car, always store aerosol products in a warm place away from extreme temperature fluctuations.
6. Musical Instruments

If you’re a musician, your instruments are probably some of your most prized possessions. Cold temperatures can wreak havoc on musical instruments, especially those made of wood or metal. Wood can crack or warp when exposed to the cold, while metal parts can contract and become brittle. For stringed instruments, like guitars, the tension in the strings can change due to the temperature, making it difficult to tune properly and even damaging the instrument. Condensation can also form inside the instrument when moving it from the cold to a warm environment, which can cause internal damage. To preserve the integrity of your musical instruments, always store them indoors where the temperature remains stable.
7. Perishable Groceries

When you leave perishable items, such as dairy, meat, or fresh produce, in your car during winter, you risk damaging them beyond repair. While it might seem like the cold temperature could preserve the food, freezing temperatures can cause fruits and vegetables to become mushy and unappetizing once thawed. Dairy products can also spoil, and the texture of meats can change, making them unsafe to eat. Moreover, if your car heats up during the day or if temperatures fluctuate, it can cause the food to thaw and refreeze, which can lead to bacterial growth. Always bring perishable groceries indoors as soon as you can to ensure they remain fresh and safe.
Final Thoughts
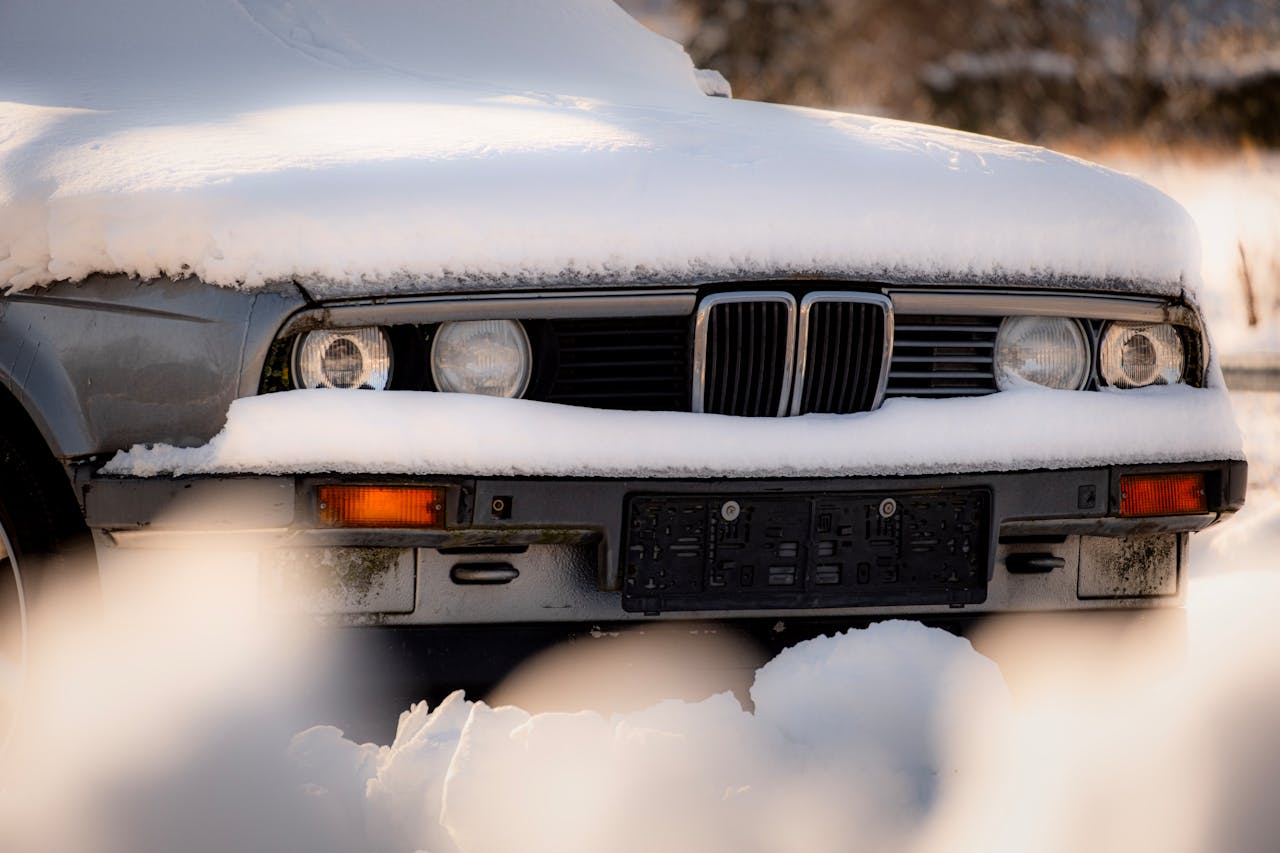

While winter may be the perfect time for hot cocoa and cozy moments indoors, it’s also a season to take extra care with the items you leave in your car. From electronics that could malfunction to medications that could lose their effectiveness, the cold can damage more than just your vehicle. By remembering to take these seven items with you instead of leaving them in your car, you can protect your belongings, save money on replacements, and keep your car organized and safe. So, the next time you’re headed out in freezing temperatures, make sure to double-check your car and take these essentials with you.

























































![3. Performance and Efficiency <p>The Tesla Model Y boasts impressive performance metrics that appeal to a wide range of drivers. With instant torque and rapid acceleration, the Model Y can go from 0 to 60 mph in just a few seconds, providing a thrilling driving experience. Additionally, the Model Y offers excellent efficiency, with a range of over 300 miles on a single charge, making it a practical option for daily commutes and long road trips alike. In contrast, while the Camry is known for its reliability, it doesn’t offer the same level of excitement or efficiency.if(typeof ez_ad_units == "undefined"){ez_ad_units=[];}ez_ad_units.push([[250,250],"ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1","ezslot_14",107,"0","0", "ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1-0"]);if(typeof __ez_fad_position == "function"){__ez_fad_position("div-gpt-ad-ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1-0");} .large-mobile-banner-1-multi-107{align-items:center;border:none !important;display:flex !important;flex-direction:column !important;float:none !important;justify-content:center;line-height:0px;margin-bottom:15px !important;margin-left:auto !important;margin-right:auto !important;margin-top:15px !important;max-width:100% !important;min-height:250px;min-width:250px;padding:0;text-align:center !important;}</p> ::Pexels](https://www.ourdebtfreefamily.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/pexels-theidahoan-2480315.jpg)









![3. Age of the Car: Nostalgic or Up-to-Date? <p>People often notice the age of a car, and this can hint at your lifestyle choices. Driving an older model might suggest that you’re nostalgic, practical, or environmentally conscious by extending the life of your vehicle. A brand-new, high-tech car, on the other hand, can indicate that you’re up-to-date with the latest trends and enjoy having the newest gadgets at your fingertips.if(typeof ez_ad_units == "undefined"){ez_ad_units=[];}ez_ad_units.push([[336,280],"ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1","ezslot_4",107,"0","0", "ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1-0"]);if(typeof __ez_fad_position == "function"){__ez_fad_position("div-gpt-ad-ourdebtfreefamily_com-large-mobile-banner-1-0");}</p> ::Pexels](https://www.ourdebtfreefamily.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/pexels-joshuaklr-757184.jpg)

























